Proven efficacy and an established safety profile for older adults1

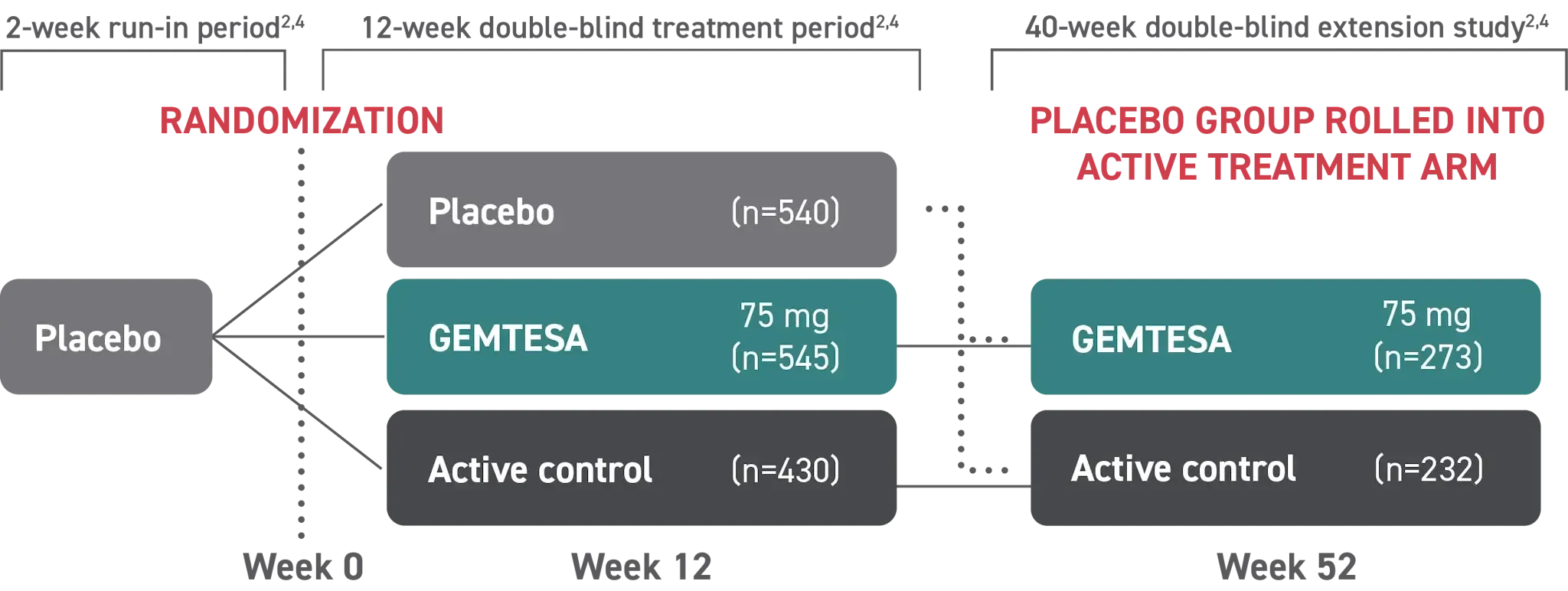
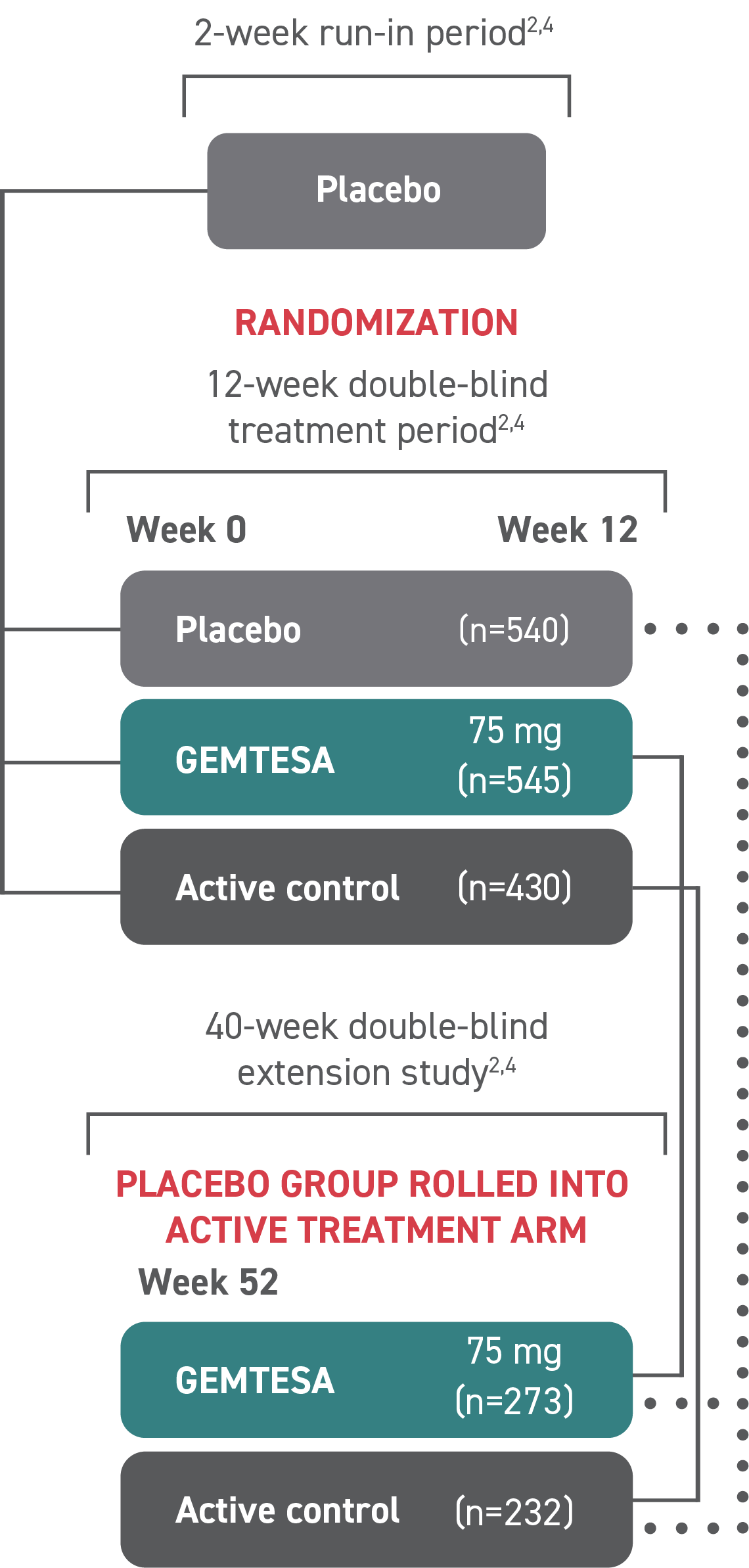
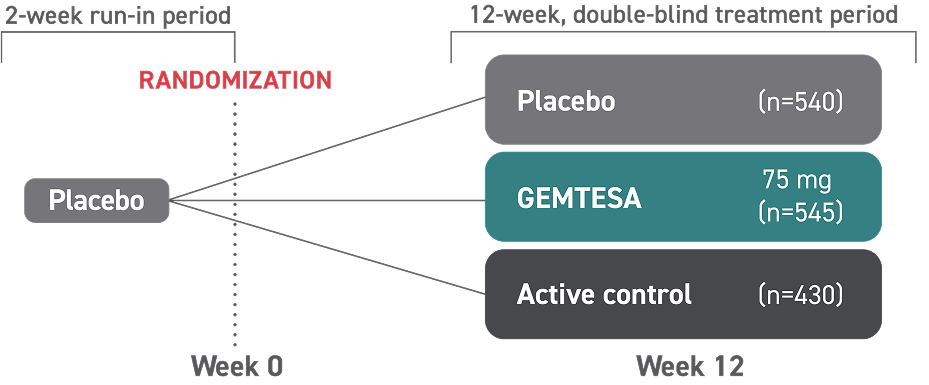
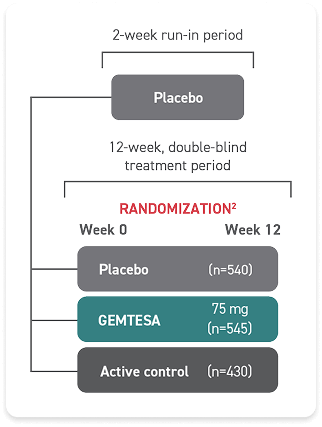
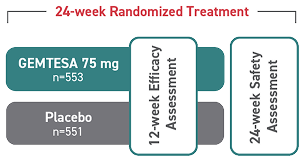
GEMTESA was evaluated at 12 weeks and 52 weeks in the overall study population2-4
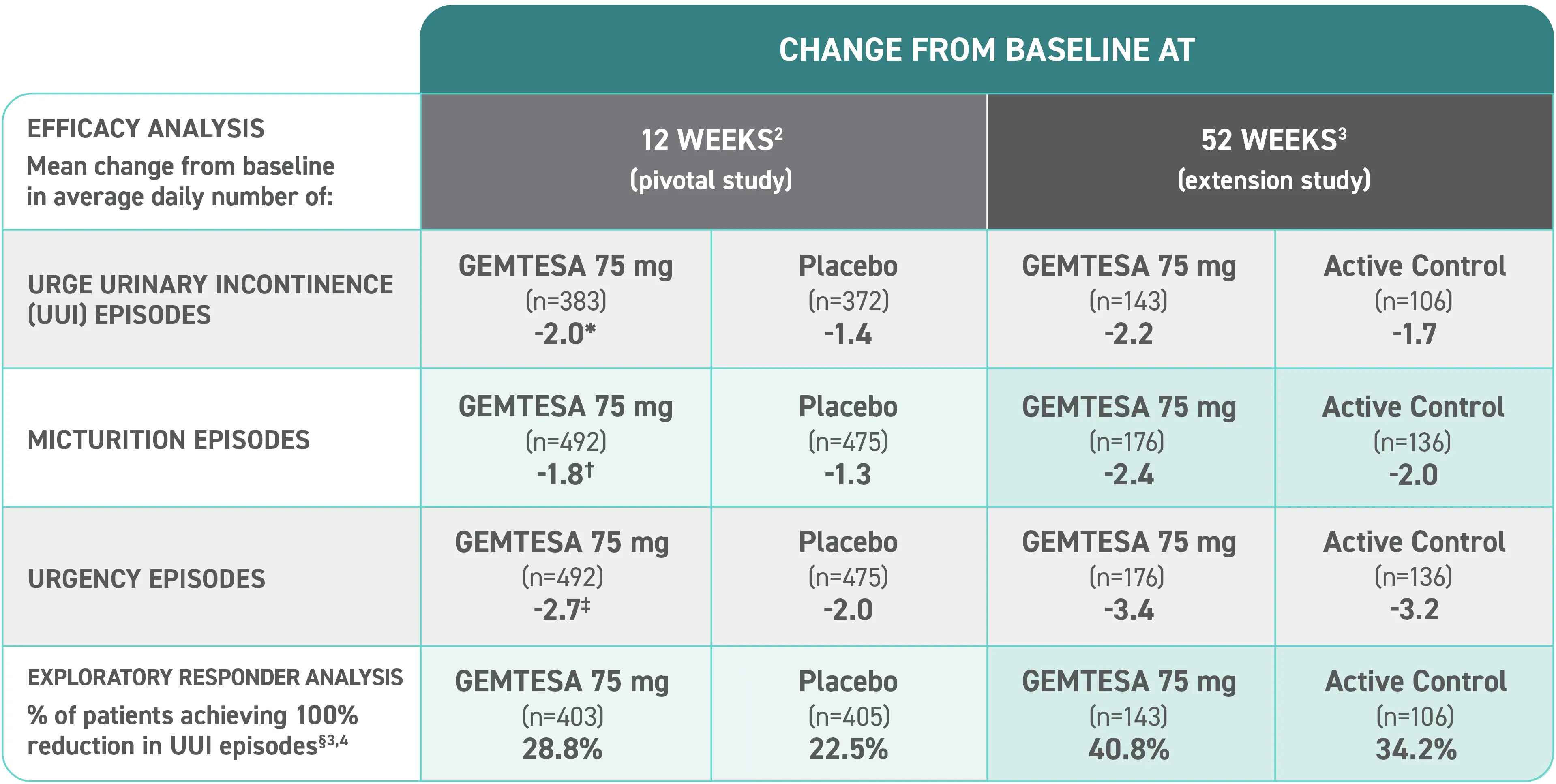
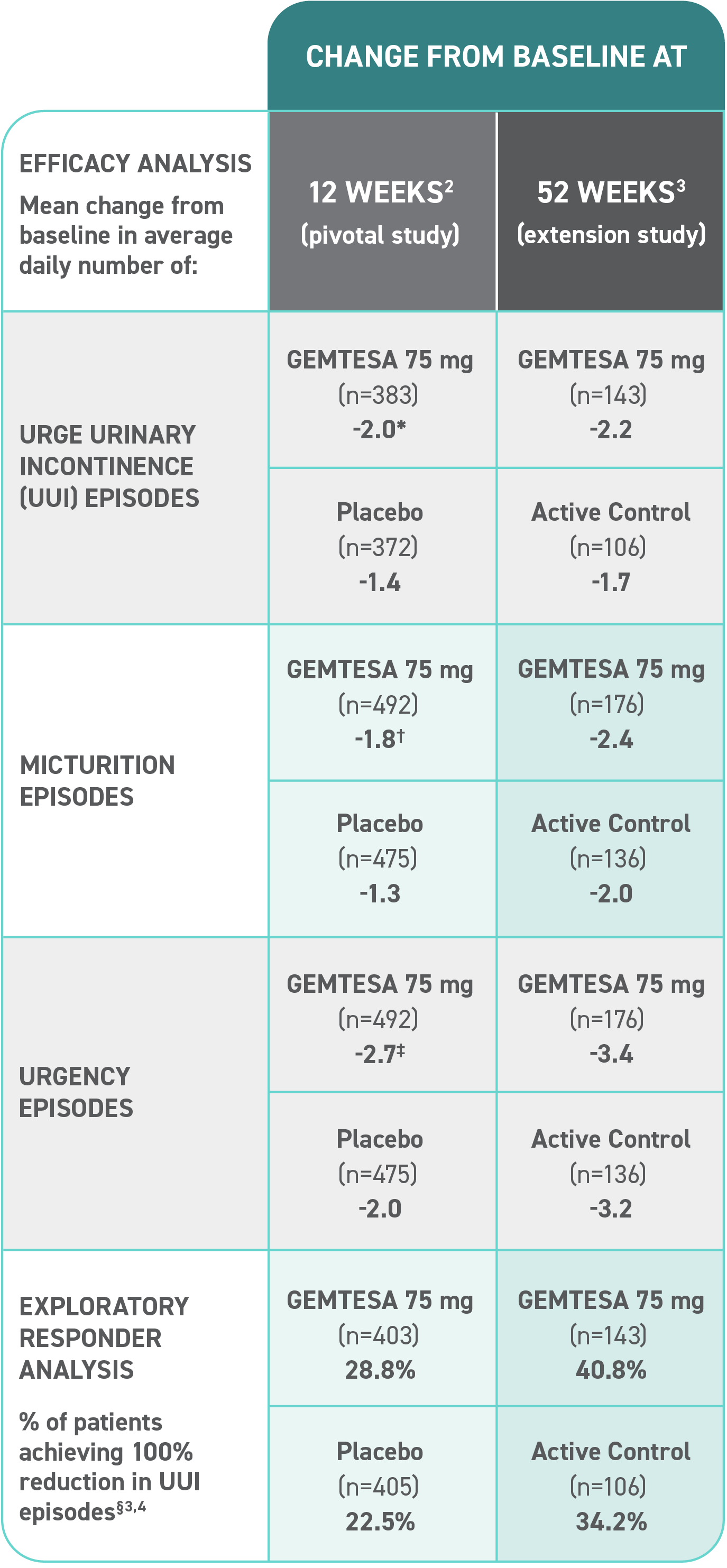
Efficacy analyses were performed using the FAS, except for incontinence episode endpoints, which used the FAS-EXT.3,5
*P<0.0001 vs placebo.2-4
†P<0.001 vs placebo.2-4
‡P=0.002 vs placebo.2-4
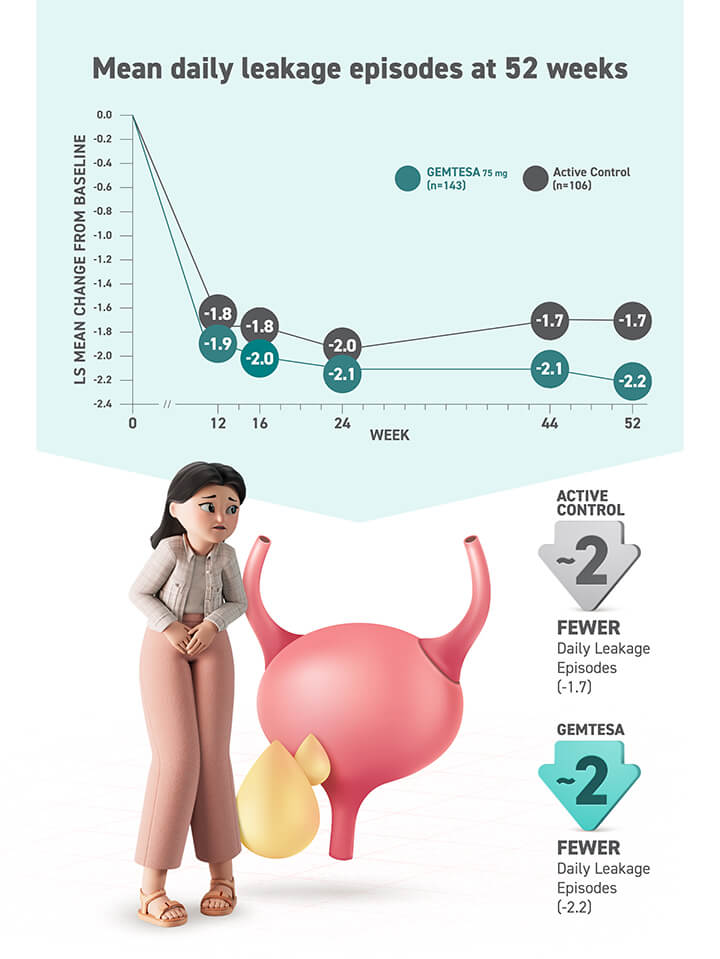
§ Data were based on an exploratory endpoint analysis of patients with 100% reduction in UUI from baseline at week 52 (n=143).4
In the older adult subpopulation, reductions in all 3 key OAB symptoms* were
Consistent with the overall study population at 12 weeks1
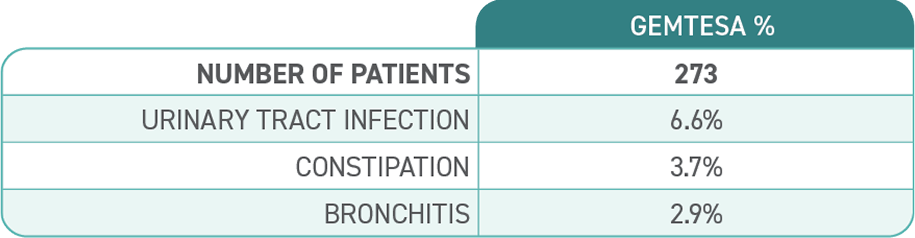
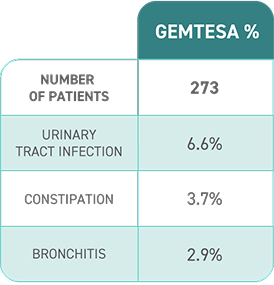
No overall differences in safety or effectiveness of GEMTESA have been observed between patients aged 65+ years and younger adult patients
This post hoc subpopulation analysis was not powered to detect differences within subgroups and is therefore limited by the small sample sizes, particularly in the subgroup of patients aged ≥75 years.
Mean daily reduction in UUI at 12 weeks in older adults1
Mean daily reduction in frequency at 12 weeks in older adults1
Mean daily reduction in urgency at 12 weeks in older adults1
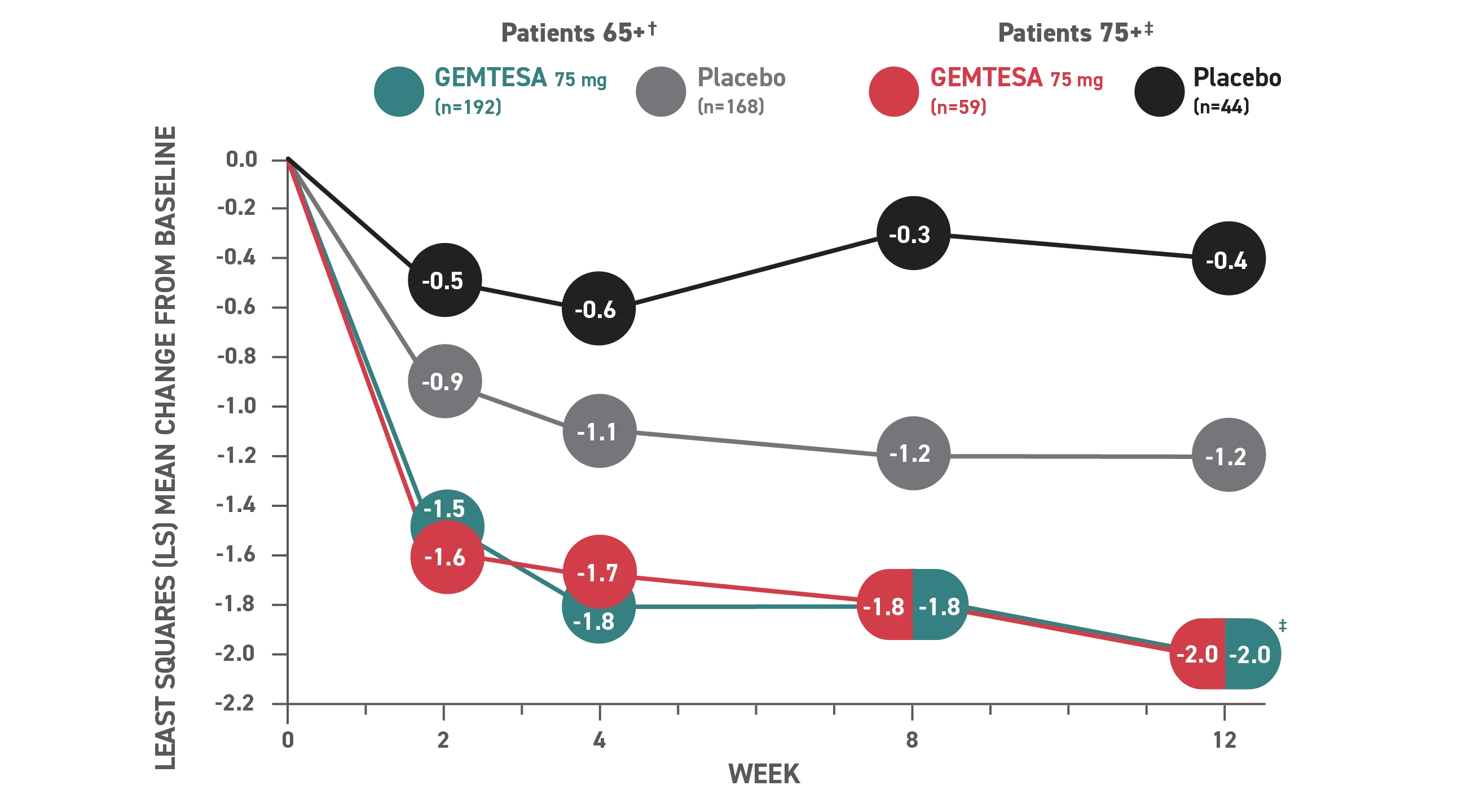
Reduction in average daily UUI/leakage episodes at 12 weeks (co-primary endpoint) vs placebo.
* OAB symptoms include urgency, frequency, and UUI.6
† Patients 65+ baseline: 3.28 for GEMTESA; 3.33 for placebo.4
‡ Patients 75+ baseline: 3.54 for GEMTESA; 2.85 for placebo.4
§P<0.001 vs placebo as Week 12.1
FAS=full analysis set; FAS-EXT=full analysis set extension; OAB=overactive bladder; UUI=urge urinary incontinence.